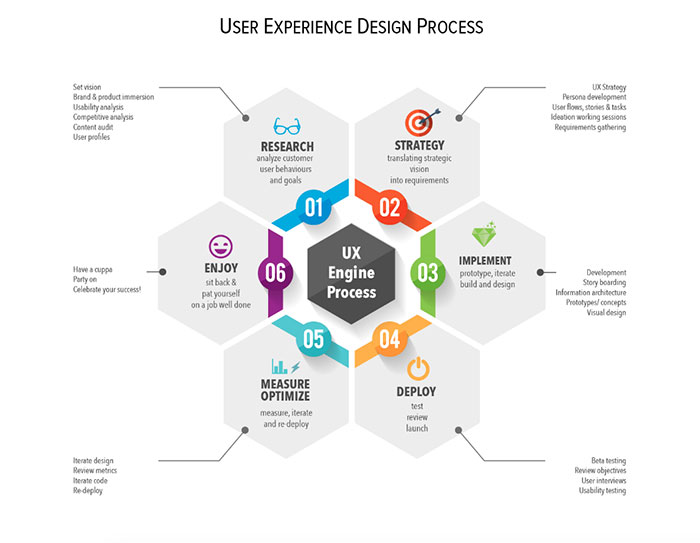
What Is UX Design And Why It’s Important

What is UX design?
UX (User Experience) design is a multidisciplinary field focused on designing products that provide meaningful, relevant, and enjoyable experiences to users.
In this article, I’ll dive deep into the world of UX design, its history, principles, process, and much more.
Table of contents
- The History of UX Design
- UX Design Principles
- Components of UX Design
- The UX Design Process
- Roles in UX Design
- UX Design Tools
- User-Centered Design Approach
- UX Design Best Practices
- UX Design Case Studies
- The Future of UX Design
The History of UX Design
Early Beginnings
The history of UX design can be traced back to the early days of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The field has its roots in ergonomics, cognitive psychology, and computer science, providing a user-centered design approach to technology.
It was during the 1980s when Don Norman, a cognitive scientist and usability engineer, coined the term “user experience,” thereby setting the stage for the development of fundamental UX design principles and usability guidelines.
Evolution of UX Design
Over the years, UX design has evolved significantly. As technology advanced, so did the needs and expectations of users.
Designers started to focus more on creating user-friendly and visually appealing interfaces, which led to the rise of web and mobile applications.
With the advent of new design tools like Figma, Sketch, and Adobe XD, designers could create high-fidelity prototypes more easily, leading to more effective usability testing techniques.
Key Milestones
Some notable milestones in the history of UX design include the development of the first graphical user interface (GUI) by Xerox PARC, the launch of Apple’s Macintosh, and the inception of the World Wide Web.
These advancements have shaped the UX design landscape we know today, introducing new UX metrics and eye-tracking studies to gauge effectiveness.
UX Design Principles
There are several fundamental principles that guide UX designers in creating effective and enjoyable user experiences. Let’s take a look at some of them.
Usability
Usability is the cornerstone of UX design. It refers to how easy it is for users to interact with a product and achieve their goals.
Good usability requires clear navigation, logical layout, and user-friendly functionality. Techniques like heuristic evaluation and task analysis often come into play here.
Consistency
Consistency means maintaining a uniform design throughout a product, conforming to usability guidelines and design system standards.
This makes it easier for users to understand and navigate the interface, as they can predict how things will work based on their previous interactions.
Feedback
Feedback is crucial in UX design. It helps users understand the results of their actions, whether it’s through visual cues like highlighting a selected button (microinteractions) or auditory signals like a beep when a task is complete. Feedback loops and user feedback surveys can provide additional insights.
Flexibility
A flexible design caters to different user preferences, skill levels, and devices.
This may involve providing multiple ways to complete a task (affordances in design), accommodating various input methods, or ensuring compatibility with different screen sizes (responsive web design).
Error Prevention
Preventing errors is an essential aspect of UX design.
This can be achieved by designing clear and straightforward interfaces, providing helpful instructions (information architecture), and incorporating safeguards like error messages and prompts to minimize the occurrence of user mistakes.
Components of UX Design
UX design is a broad field that encompasses various components. Let’s explore some of the key elements that contribute to a well-rounded user experience, ranging from information architecture to emotional design and touchpoint optimization.
Information Architecture
Information Architecture (IA) deals with the organization and structure of content within a product. This aspect of UX design focuses on heuristic evaluation and task analysis to help users find the information they need quickly and easily, thus enhancing the overall user experience.
Interaction Design

Interaction design focuses on the way users interact with a product, such as how they input data, navigate through menus, or complete tasks. A good interaction design ensures that these interactions are seamless and intuitive, utilizing microinteractions and feedback loops to guide user actions.
Visual Design
Visual design is the aesthetic aspect of UX design. It involves the use of colors, typography, imagery, and other design elements like Gestalt principles to create an appealing and functional interface.
Content Strategy
Content strategy is the planning, creation, and management of content within a product. It ensures that the information presented to users is relevant, engaging, and easy to understand. This is where content strategy overlaps with SEO and information architecture, aiming for clear navigation and user-friendly functionality.
User Research
User research is a crucial component of UX design. It involves gathering insights about users’ needs, preferences, and behaviors through various methods, such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing techniques. These insights help designers make informed decisions and create user experiences that meet the target audience’s needs and expectations.
The UX Design Process
The UX design process is a series of steps that designers follow to create user-centric products.
While the exact process may vary depending on the project and organization, the following stages are commonly involved, influenced by Agile methodology and Scrum framework practices.
Discovery
During the discovery phase, UX designers from a UX design agency gather information about the project’s goals, target audience, and competition.
They also conduct user research to gain insights into users’ needs and pain points, often utilizing ethnographic studies and customer journey analysis.
Define
In the define phase, designers analyze the research findings and identify key insights.
They create personas, user stories, and other artifacts that help them define the problem they need to solve and establish clear design objectives, thereby paving the way for a minimum viable product (MVP).
Design
The design phase involves creating wireframes, mockups, and high-fidelity prototypes to visualize the user interface and interactions.
Designers iterate on their designs, incorporating feedback from stakeholders and users to refine the solution.
Modern design tools like Figma, Sketch, and Adobe XD are commonly used at this stage.
Develop
Once the design is finalized, it moves into the development phase. Developers work closely with designers to implement the interface, ensuring that it aligns with the design vision and adheres to usability standards and guidelines.
Front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are often employed here.
Test
In the testing phase, UX designers conduct usability testing to evaluate the product’s performance and identify any issues that need to be addressed.
Techniques such as A/B testing methods and eye-tracking studies may be used to collect valuable data.
Launch
Once the product is thoroughly tested and refined, it’s ready for launch.
Designers may continue to monitor its performance through UX metrics, gather user feedback surveys, and make updates as necessary to ensure ongoing success and customer retention.
Roles in UX Design
There are various roles within the UX design field, each with its own set of responsibilities and areas of expertise, ranging from interaction design to accessibility considerations. Some of the most common roles include:
UX Designer

A UX designer is responsible for the overall user experience of a product, covering everything from heuristic evaluations to user testing.
They conduct user research, create user flows, wireframes, and high-fidelity prototypes, and collaborate with other team members, like developers and stakeholders, to bring the design to life.
By the way, companies that prioritize UX often use this UX design test from Testgorilla to assess the expertise of the professionals they’re entrusting to this critical aspect of their website or application. You might find it useful.
UI Designer
A UI designer focuses on the visual aspects of a product, such as layout, color schemes, typography, and icons. They may also delve into aspects like Gestalt principles and visual hierarchy.
They work closely with UX designers to ensure the interface is visually appealing and supports the overall user experience strategy.
UX Researcher

A UX researcher specializes in gathering and analyzing both qualitative and quantitative data about users through methods like ethnographic studies and usability testing.
They conduct various research methods to understand users’ needs, behaviors, and preferences, which inform and shape the design process.
Before establishing your strategy, you should consider incorporating valuable UX research strategy tips to establish a strong foundation for effective user research, ultimately driving successful design outcomes.
If you’re considering upskilling, there’s an actual UX Design Professional Certificate course by Google on Coursera. Why would you want that? Well, what if I told you that there are over 138,000 open jobs in UX design, and the median entry-level salary is around $112,000?
UX Writer
A UX writer is responsible for crafting the microcopy within a product, such as labels, CTA buttons, instructions, and error messages.
They collaborate with designers and developers to ensure the content is clear, concise, and supports the user journey and task flow.
Interaction Designer
An interaction designer focuses on designing the interactive touchpoints and feedback loops that dictate the way users interact with a product, from clickable buttons to swiping gestures and haptic feedback.
They ensure that these interactions are intuitive, efficient, and add to an enjoyable user experience.
UX Design Tools
There are numerous software tools and applications available to UX designers for designing user interfaces, each with its own set of features, usability attributes, and capabilities for enhancing user satisfaction. Some popular UX design tools include:
Sketch
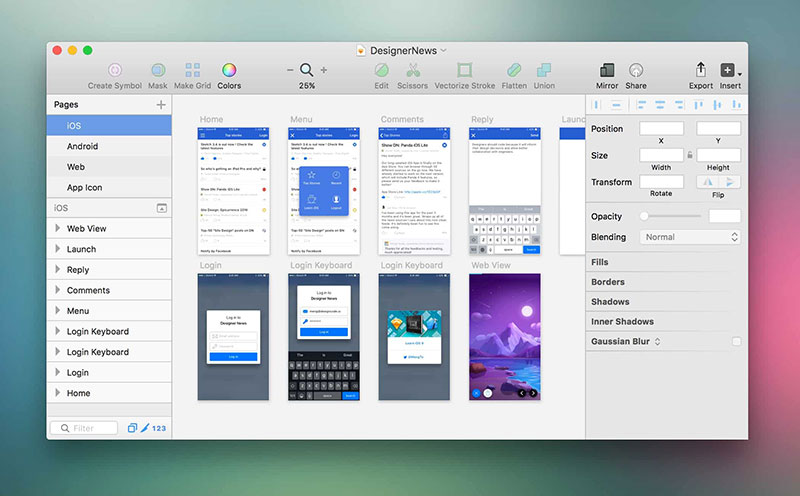
Sketch is a vector-based design tool primarily used for creating wireframes, mockups, and high-fidelity prototypes. It offers a range of features, such as layers and artboards, and plugins that make it a popular choice among UX/UI designers for project management.
Figma
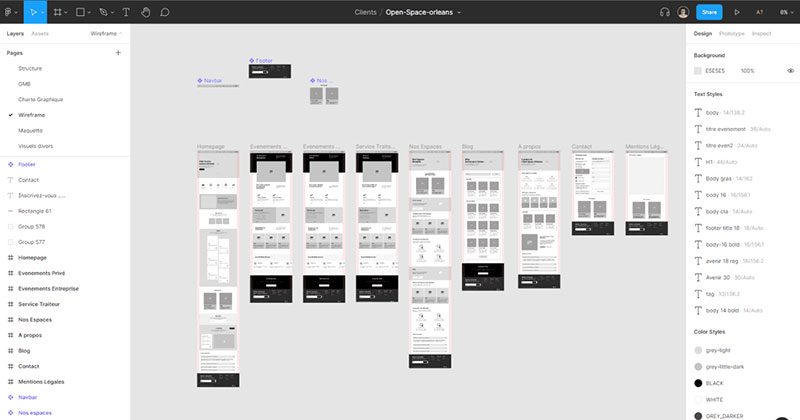
Figma is a cloud-based design tool that allows designers to collaborate in real-time, ideal for remote teams. It supports wireframing, prototyping, and design systems, making it a versatile option for UX design teams. Figma provides plugins and features that enable even developers to convert Figma to Flutter code.
Adobe XD
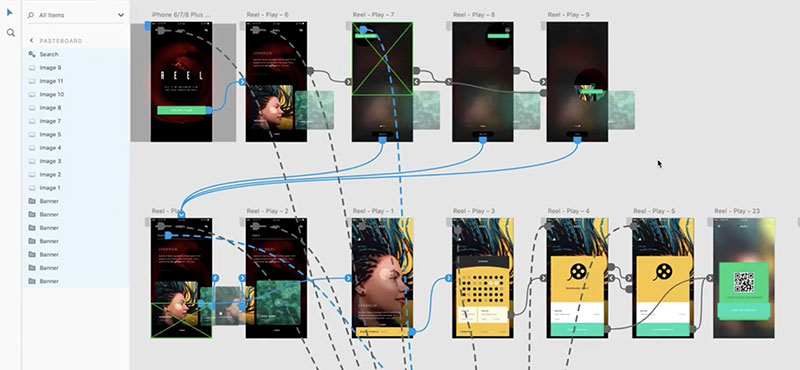
Adobe XD is a design and prototyping tool that’s part of Adobe’s Creative Cloud suite. It offers features such as repeat grids, auto-animate, and voice prototyping, which streamline the design process, making it suitable for user interface design and A/B testing.
InVision
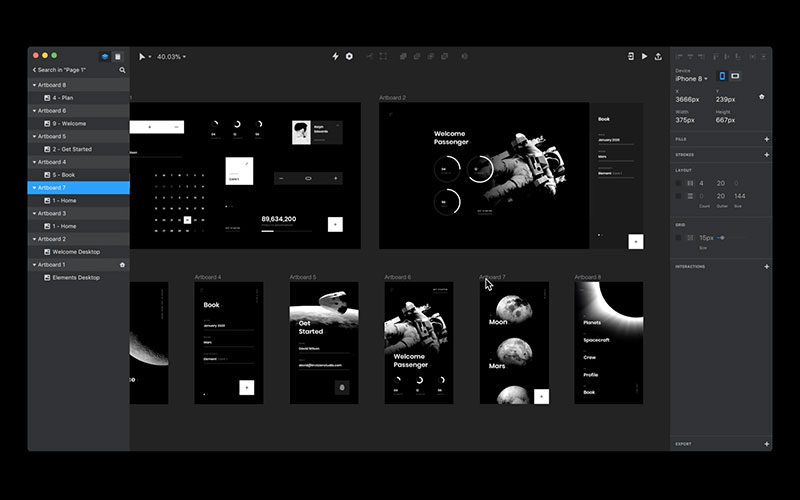
InVision is a design and prototyping platform that supports collaboration between designers and stakeholders, ideal for the agile development process.
It offers features like boards, interactive prototypes, and design systems, making it an excellent tool for managing design projects and sharing progress with team members, especially during sprint reviews.
User-Centered Design Approach
A user-centered design approach emphasizes the needs and preferences of users throughout the design process, focusing on human factors and the end-to-end customer journey. It involves:
Understanding Users
By conducting in-depth user research, designers can gather valuable insights into users’ needs, behaviors, emotional triggers, and expectations through data analytics and persona development.
This information helps inform the design process, ensuring that the product is tailored to its target audience and their user scenarios.
Designing for User Needs
User-centered design involves creating empathetic solutions that address the specific needs, pain points, and requirements of users, utilizing techniques such as wireframing and heuristic analysis.
Designers prioritize functionality, usability, and accessibility, focusing on navigational elements to ensure a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
Evaluating Designs with Users
An essential part of the user-centered design process is usability testing and iterating on designs based on user feedback and task analysis.
This helps identify and address any issues or roadblocks, ensuring that the final product aligns with user satisfaction and meets the needs of its users.
UX Design Best Practices
There are several best practices and fundamental principles that UX designers should follow to create successful, efficient, and meaningful user experiences. Some of these include:
Accessibility
Designing for accessibility ensures that products are usable by people with different abilities, such as visual impairments or motor disabilities.
This encompasses providing alternative text for images, ensuring proper contrast ratios, and designing for keyboard navigation, thereby enhancing overall user satisfaction.
Responsive Design
Responsive design involves creating interfaces that adapt to different screen sizes, devices, and orientations.
This ensures a consistent, scalable, and enjoyable user experience, regardless of the device or platform being used.
User Testing
Conducting regular user testing and usability analysis is crucial for identifying potential issues, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement in the user experience.
Through A/B testing and gathering feedback from users, designers can make data-driven decisions and iterate on their designs more effectively.
Designing for Emotion
Emotion plays a significant role in user experience and customer journey mapping. By designing for emotion, designers can create more engaging, memorable, and resonant experiences that trigger positive emotional responses from users.
Iterative Design
Iterative design is the process of refining, improving, and evolving a product through multiple iterations, sprints, and user feedback sessions.
This agile approach allows designers to learn from user insights and continually refine their designs, resulting in a more polished and effective end product.
UX Design Case Studies
Examining successful and unsuccessful UX designs through case studies can provide valuable insights and lessons learned into what works and what doesn’t. Some examples include:
Successful UX Designs
Examples of successful UX designs might include popular apps like Airbnb, Spotify, and Uber.
These products have been praised for their intuitive interfaces, seamless user flows, user-centric design, and overall enjoyable and efficient user experiences.
UX Design Failures
On the flip side, some digital products have faced criticism for their poor UX designs, such as confusing navigation, cluttered interfaces, or a lack of user feedback mechanisms, leading to frustration and negative user experiences.
Lessons Learned
By studying these case studies and reviewing user scenarios, UX designers can glean valuable lessons and best practices to avoid making similar mistakes in their own work.
FAQ on UX Design
What’s UX Design, Man?
So, you’re curious, huh? UX Design, or User Experience Design, is basically the art and science of crafting an experience that’s easy, efficient, and enjoyable for the user.
Think of it as a roadmap that guides you from point A to point B. It’s not just about pretty colors or cool fonts; it’s about understanding the user’s needs and solving their problems.
Yeah, it’s the good stuff that keeps users coming back for more.
Why’s it So Important?
Alright, let me break it down. When you’re building a product or a service, the user’s experience can make or break its success.
Bad UX?
You’re pretty much shooting yourself in the foot. On the flip side, good UX can lead to higher user engagement, increased revenue, and even brand loyalty.
You get more bang for your buck, if you get what I mean.
How’s it Different from UI Design?
Ah, the age-old question. UX and UI are like siblings; close but not the same. UX focuses on the overall journey and how the user feels throughout.
UI, or User Interface, zeroes in on the actual elements that users interact with—buttons, icons, you name it.
UI is about the visual aesthetics, while UX is the full emotional and functional spectrum.
What’s a User Persona?
You’ve got to know who you’re designing for, right? A user persona is basically a fictional character that represents your typical user.
This ain’t just some make-believe; it’s built on real user data and research. Helps you empathize with the users and tailor the experience to meet their specific needs.
What Tools Do UX Designers Use?
Tools, tools, tools! From wireframing to prototyping, we’ve got software like Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma.
Then there’s the good ol’ user testing platforms and even some project management stuff like Jira or Asana. The toolkit can be as simple or as complex as the project demands.
What are UX Design Principles?
Alright, principles are like the Ten Commandments for UX designers. Stuff like “Put Users First,” “Simplicity is Key,” and “Consistency Matters” guide the design process.
These are your North Star; they help you stay focused on creating meaningful and effective experiences.
What’s User Testing?
Want to know if you’re on the right track? User testing is your go-to. It involves real users interacting with your product and giving feedback.
You can do it through various methods—interviews, questionnaires, or even watching them use the product. It’s like a reality check for your design.
How Do I Get Into UX Design?
So, you wanna join the club, huh? No one path leads to UX design; it’s a multidisciplinary field. You can come from graphic design, psychology, or even anthropology.
Online courses, bootcamps, and formal education can all get you there. Just be ready to be a perpetual learner.
What’s a UX Portfolio?
A portfolio is your golden ticket. It showcases your skills, your thought process, and your ability to solve real-world problems.
It’s more than just a collection of pretty pictures; it tells the story of each project from conception to execution. Makes you stand out from the crowd.
What are Key Metrics in UX?
If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it, right? Key metrics in UX usually include things like user engagement, task success rate, and even good ol’ customer satisfaction.
These numbers help you understand if you’re hitting the mark or need to go back to the drawing board.
Conclusion: Understanding What is UX Design and Its Significance
In conclusion, what is UX design? It’s the interdisciplinary process of creating user-centric digital products that provide meaningful, enjoyable, and efficient experiences.
With its roots in ergonomics, cognitive psychology, human-computer interaction, and computer science, UX design has come a long way and now encompasses a wide range of components, principles, and user research methodologies that guide designers in their work.
By understanding the history, principles, tools, processes, and roles within UX design, we can better appreciate its significance in the digital landscape.
As technology continues to evolve, UX designers will need to adapt, upskill, and stay ahead of emerging trends to create products that resonate with users and stand the test of time.
To learn more about user experience, try reading from sites that post regularly on this subject, like 52 weeks of UX, UX Booth, or UX Mag.
- The Epic Games Logo History, Colors, Font, And Meaning - 24 April 2024
- Spread Joy: Happy Color Palettes for Uplifting Designs - 24 April 2024
- The Konami Logo History, Colors, Font, And Meaning - 23 April 2024